Bone health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, contributing to our ability to move, support our body weight, and protect vital organs.
As we age, maintaining strong and healthy bones becomes increasingly important to prevent fractures, osteoporosis, and other bone-related issues, especially in women.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting bone health, providing the essential nutrients needed for bone formation, maintenance, and repair.
Promoting Bone Health through Nutritional Strategies
Being in my 40s, I have been consulting a nutrition specialist to learn about the natural ways to promote bone health. Diet impact on bone strength is obvious and today I am sharing with you a few tried and tested Bone-strengthening nutrient tips and strategies that can effectively promote bone health.
Make sure to include Calcium: The Building Block of Bones
A balanced diet and bone health go hand in hand. Calcium is perhaps the most well-known nutritional factor for bone health. It’s the primary mineral that makes up the structural framework of bones.
While dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich sources of calcium, individuals who are lactose intolerant or follow a vegan diet can opt for plant-based sources of calcium alternatives such as almond, soy, or oat milk. Leafy green vegetables like broccoli, kale, and bok choy also offer substantial amounts of calcium.
Research suggests Incorporating these foods into your diet can help you prevent bone loss through nutrition and ensure a sufficient intake of calcium to support bone health.
Don’t Neglect Vitamin D: Enhancing Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D and bone health are linked to one another and is a crucial partner to calcium, as it enhances calcium absorption in the intestines. The body can naturally produce vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
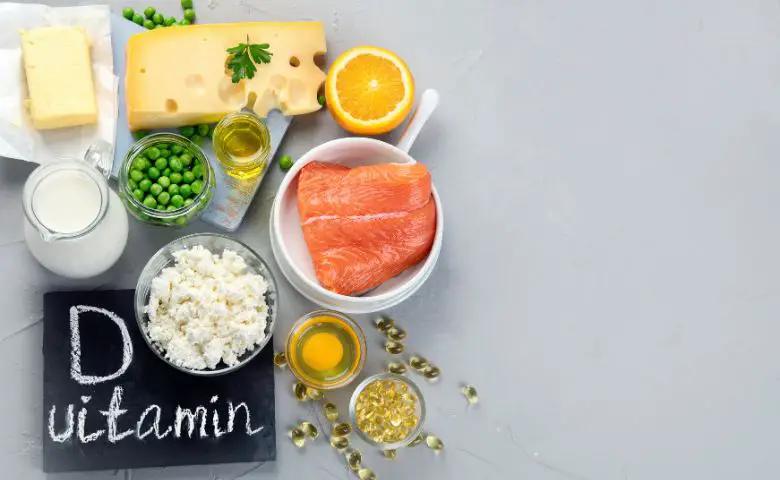

However, factors such as geographic location, season, and sun protection practices can affect the body’s ability to synthesize vitamin D. Therefore, it’s essential to include dietary sources of vitamin D in your diet to promote strong bones in women and men.
Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are excellent sources, as are egg yolks. Additionally, many foods are fortified with vitamin D, including fortified dairy and plant-based milk, orange juice, and cereals.
In cases of inadequate sun exposure or dietary intake, a vitamin D supplement can be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Magnesium is a must: Supporting Bone Mineralization
Magnesium is often overshadowed by calcium and vitamin D but is equally a bone-strengthening nutrient. This mineral plays a vital role in converting vitamin D into its active form, which is necessary for calcium absorption.

Moreover, magnesium is involved in bone mineralization and supports the structure of bones. Foods rich in magnesium include nuts, seeds, whole grains, dark leafy greens, and legumes.
Ensuring an adequate intake of magnesium can contribute to overall bone health.
Phosphorus: Bone-friendly mineral
Phosphorus is another mineral that works in tandem with calcium to strengthen bones. Fortunately, most diets already provide sufficient phosphorus through sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.

Maintaining a balanced intake of both calcium and phosphorus is crucial for bone density maintenance.
Protein: The Bone Builder
Protein is essential for bone formation and repair. Collagen, the protein matrix of bone, provides a scaffold for minerals like calcium to attach to, forming the bone’s structure.
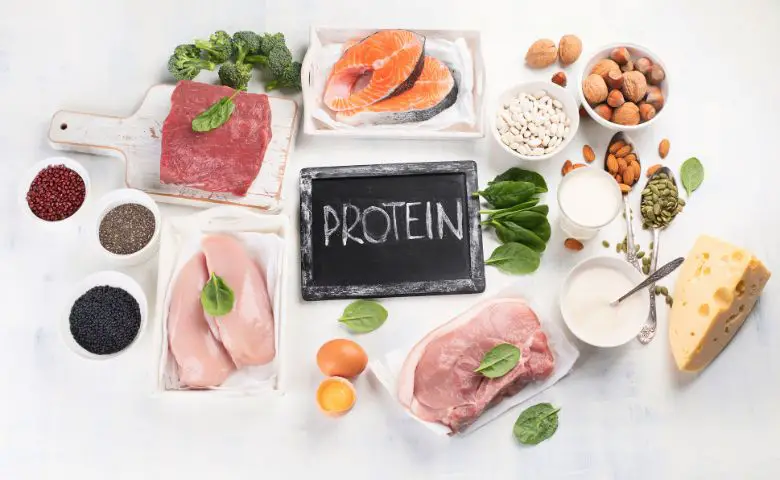

Including lean protein sources in your diet, such as poultry, fish, lean meats, beans, lentils, and soy products, can contribute to maintaining strong bones.
However, it’s important to strike a balance, as excessive consumption of red meat might have negative effects on bone health.
Limiting Sodium and Caffeine: Preserving Bone Health
Excessive sodium intake can lead to increased calcium excretion through urine. Processed foods and canned soups are often high in sodium, so it’s advisable to reduce their consumption.

Similarly, excessive caffeine intake can also result in calcium loss through urine. While moderate caffeine consumption is generally considered safe, it’s a good idea to limit excessive coffee, tea, and soda consumption to help better sleep, women’s health, and bone nutrition.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Anti-Inflammatory Support
Omega-3 fatty acids and bone health are linked together. Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can contribute to bone health.
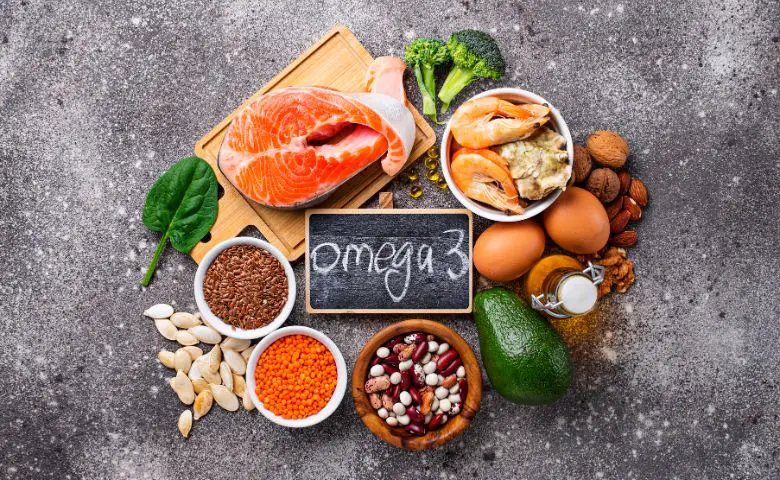

These healthy fats are found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts. Omega-3 fatty acids play a role in reducing inflammation and supporting bone density, which is essential for preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
Vitamin K: Supporting Bone Metabolism
Vitamin K is a lesser-known nutrient that plays a crucial role in women’s skeletal strength. It’s involved in bone metabolism and calcium regulation.
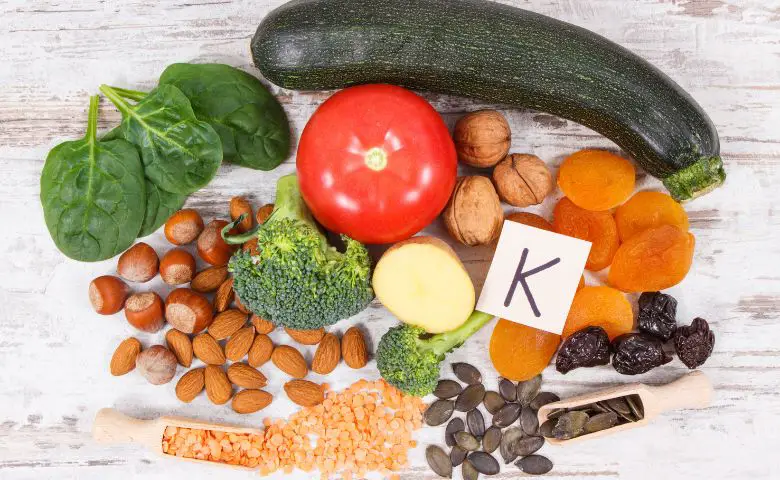

Leafy greens like spinach and kale, as well as broccoli and Brussels sprouts, are excellent sources of vitamin K. Including these foods in your diet can help support optimal bone health.
Fruits and Vegetables: Antioxidant Support
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and cellular damage, contributing to overall bone health.

The variety of vitamins and minerals in colorful fruits and vegetables supports various bodily functions, including those related to bones. Incorporating a diverse range of fruits and vegetables into your diet can provide a broad spectrum of nutrients that support bone health.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: A Cautionary Note
Excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact bone health by reducing calcium absorption and affecting bone remodeling.

It’s important to limit alcohol intake to support strong bones. If you choose to consume alcohol, do so in moderation and consider its potential impact on bone health.
Hydration: Supporting Nutrient Transport
Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for various bodily functions, including bone health. Water helps transport nutrients to cells and supports overall physiological processes, which indirectly contribute to bone health.

Ensuring proper hydration is a simple yet often overlooked aspect of promoting the importance of bone health in females.
Physical Activity: The Bone-Strengthening Factor
In addition to proper nutrition, engaging in regular physical activity is essential for promoting bone health. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and weightlifting, stimulate bone formation and help maintain bone density.

These activities exert mechanical stress on bones, triggering the body to reinforce bone structure. Incorporating a variety of weight-bearing exercises into your routine can contribute to maintaining strong and healthy bones.
Related: 7 Best At Home Workouts For Busy Moms To Look And Feel Great
If you’re a busy mom with a kid and can’t seem to find the right exercise for yourself then here are some awesome mommy and me exercises for you that get your baby on board with you so you don’t have to worry about leaving your little one anywhere.
Wrapping up on Bone-friendly foods for women
So, here are my female bone health tips for you all. Bone-friendly foods for women are a holistic approach that encompasses various nutritional strategies and dietary choices for strong bones.
A well-balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and other essential nutrients, combined with regular physical activity, is key to supporting optimal bone health throughout life.
However, if you are facing some serious health issues, read about bone health guidelines for women, and consult a healthcare professional or registered nutritionist who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific nutritional needs.
By prioritizing bone health through nutrition and lifestyle choices, you can enjoy the benefits of strong and resilient bones, contributing to your overall well-being and quality of life.
Related Articles:
13 Affordable Stress Relief Ideas For Moms
7 Best At Home Workouts For Busy Moms To Look And Feel Great
10 Ways To Boost Your Family’s Immune System
13 Ways To Invest In Yourself As A Mom
15 Top Foods That Help You Sleep Better
10 Health And Fitness Tips For Busy Moms
Mommy and Me Exercises: Fun Ways to Bond and Get Fit with Your Baby With Videos
Nutrition During Pregnancy: 14 Best Foods To Eat
Don’t forget to pin it for later!

Unlocking Stronger Bones: 12 Essential Nutrition Tips for Women’s Bone Health
Jaishree Nenwani
She is the author of a self-help book “Tiny Habits Massive Results”. Based out of New Delhi, India Jaishree is an Author, blogger, and homepreneur. She is passionate about journaling and is a health enthusiast. She loves to share wisdom and journaling tools that invoke deeper authenticity and Personal transformation. She writes about Women’s Health, Self-improvement, Personal growth, and ways to become happier in your life. Connect with on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter or Linkedin.

What an excellent blog post on bone health! Thank you for sharing these valuable tips. Your emphasis on a balanced diet, including calcium-rich foods, alternatives for various dietary preferences, and the significance of vitamin D, is spot on.
I appreciate your advice on protein, sodium, caffeine, and the importance of Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin K, and antioxidants. The caution about alcohol consumption, hydration, and the value of weight-bearing exercises are also critical points.
Your dedication to well-researched information and encouraging personalized guidance from healthcare professionals is commendable. Keep up the great work; your blog is a valuable resource. Thanks for sharing this essential information!
Thank you so much! Glad you liked it
Yes, I realize now, at 39 years old, that vitamin D is essential to get calcium. Strangely, I’m Canadian and moved to Spain, and I go out plenty but still have a deficiency in Vitamin D… so strange. Anyhow, I need some pills, but I will try to add more food supplements like fish and eggs. Thanks for the info; it’s beneficial.
You can definitely incorporate tuna in your diet which is easily available. That will help with vitamin D deficiency.
I’m having trouble getting the pinning off the website thing down but I think I got it through a back door. I am on Vit. D3, magnesium and B12. Interesting how they all interact.